

The following diagram provides a conceptual overview of how this works: For more information, see : Windows Update Services: Server-Server Protocol.įor more information about the CSPs, see Update CSP and the update policy area of the Policy CSP. The MDM will want to show IT-friendly information about the update, instead of a raw GUID, including the update’s title, description, KB, update type, like a security update or service pack. The Update ID is a GUID that identifies a particular update. The OMA DM APIs for specifying update approvals and getting compliance status refer to updates by using an Update ID. Approve end-user license agreements (EULAs) for the end user so update deployment can be automated even for updates with EULAs.

The list makes sure devices only install updates that are approved and tested.
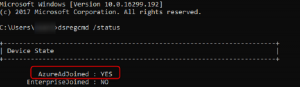
IT can understand which machines still need a security patch, or how current is a particular machine. Get compliance status of managed devices.Test updates on a smaller set of machines by configuring which updates are approved for a given device.Ensure machines stay up to date by configuring Automatic Update policies.In particular, Windows 10 provides APIs to enable MDMs to: One key feature we're adding is the ability for MDMs to keep devices up to date with the latest Microsoft updates. In Windows 10, we're investing heavily in extending the management capabilities available to MDMs. With PCs, tablets, phones, and IoT devices, Mobile Device Management (MDM) solutions are becoming prevalent as a lightweight device management technology. If you're not a developer or administrator, you'll find more helpful information in the Windows Update: Frequently Asked Questions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
